Base rate reduced to 14.75%
The Monetary Policy Committee of the National Bank of Kazakhstan decreased the base rate by 50 basis points and has set it at 14.75% with a corridor of +/-1 percentage point.
Annual inflation continued to decline in January. Inflation expectations have been slowing down for three consecutive months. Thus yet, monthly inflation is above its historical average. The external inflation environment is developing neutrally. Inflation accelerated insignificantly in a number of trading partners, slightly increasing external inflationary pressures. A continued decline in world food prices positively contributes to the external inflation environment. Inflationary pressures persevere in the domestic economy due to persisting domestic demand and unanchored inflation expectations.
In the current environment there is limited room for monetary policy easing. Conditioned on the present arrangement of factors of inflation, its current (monthly) dynamics, and uncertainties in fiscal policy parameters, there is a high probability of retention of the base rate at its current level in the nearest decisions. Collecting data and monitoring the implementation of economic and fiscal reforms is required.
In January 2024, annual inflation subsided to 9.5%, in line with the National Bank’s forecast. The slowdown in overall price growth is conditioned on implemented monetary policy, decrease in global inflationary pressure and production costs, gradual restoration of logistics chains, government measures, and the last year’s high base effect.
Monthly inflation of 0.8% evolved higher than the historical average (0.6%). Core inflation as an indicator of the stable component of consumer prices, and seasonally adjusted inflation somewhat accelerated and remained above the target level.
A positive factor behind the base rate cut was the population's inflation expectations, which noticeably decreased in January and have been slowing for the third consecutive month.
The overall external inflation environment is developing neutrally. Global inflation is slowing down as a result of decreasing world food and energy prices. Concurrently, inflation is at a high level in Russia, there is an increase of monthly inflation in China. The FAO food price index abated in January against the backdrop of lower prices for grains and meat. Despite the slowdown in global inflation, external monetary conditions remain tight. The US Federal Reserve and the ECB are reluctant to cut rates due to necessity of inflation returning to its target.
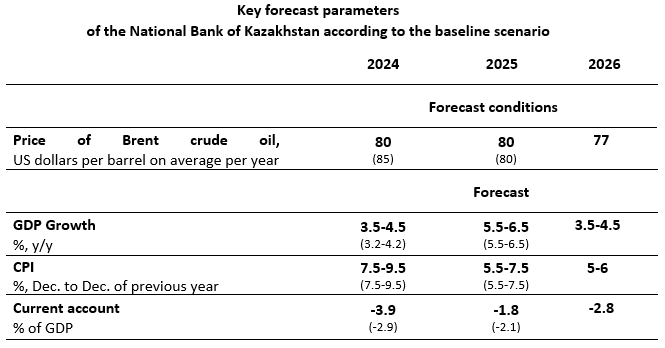
The baseline scenario assumes the stabilization of Brent crude oil prices by the end of 2025 at $80 per barrel conditioned on continued OPEC+ production cuts, moderate extraction by the US and ongoing military actions in the Middle East. It is expected that oil prices will decrease slightly in 2026 to annual average of $77 per barrel. Besides, this scenario envisions a slight increase in world food prices (the FAO grain price index) until mid-2024, followed stabilization and then a gradual decrease of prices. The prerequisites reflect both the risks of possible logistical problems in the Red and Black Seas from one side and the FAO forecasts for crop prospects and global growth of grain stocks at the end of 2024 season from another side.
Inflation forecasts remain unchanged in the range of 7.5-9.5% in 2024 and within 5.5-7.5% in 2025. In 2026, inflation is projected within the scope of 5-6%. Main risks around the inflation outlook are associated with uncertainty of fiscal policy parameters, persisting inflation dynamics coupled with unanchored inflation expectations, and possible new sanctions against trading partners.
Following current developments, Kazakhstan’s economic growth forecast for 2024 has been raised to 3.5-4.5%, while the outlook for 2025 is maintained in the range of 5.5-6.5%. Economic growth in 2024 will be driven by domestic demand on the backdrop of improvements in business activity. Expansion of production in TCO and the subsequent rise in oil extraction will be a key determinant of economic growth in 2025. In 2026, with a scenario decline in oil prices and current forecast assumptions, GDP growth rates will account to 3.5-4.5%. GDP growth and inflation projections are subject to revision as far as Kazakhstan’s new economic policy is formulated and implemented.
The National Bank is committed to achieving the inflation target of 5% in a medium-term. This requires maintaining a moderately tight monetary policy for a longer period. In this regard, the room for further monetary policy easing is significantly limited given the current environment. Conditioned on the present arrangement of factors of inflation, its current (monthly) dynamics and uncertainties of fiscal policy parameters, there is a high probability of maintaining the base rate at its current level in nearest policy decisions. The National Bank will monitor incoming economic data and continue observing the implementation of reforms and the balance of risks.
The key parameters of the forecast are provided in the appendix. Detailed information on the determinants of the decision and forecast will be provided in the Monetary Policy Report on the official Internet resource of the National Bank on March 4, 2024.
The next planned base rate decision of the Monetary Policy Committee of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan will be announced on April 12, 2024 at 12 pm (Astana time).
Detailed information for the mass media representatives is available upon request:
+7 (7172) 775 205
e-mail: press@nationalbank.kz
www.nationalbank.kz
Appendix